Based on recent reports, the Indian Navy’s second nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN) is expected to enter service in the upcoming months, over seven years after being launched by the Shipbuilding Centre (SBC). This aligns with a February 2023 report by the Hindustan Times, which announced that the submarine would enter service this year as part of the indigenous submarine development program.
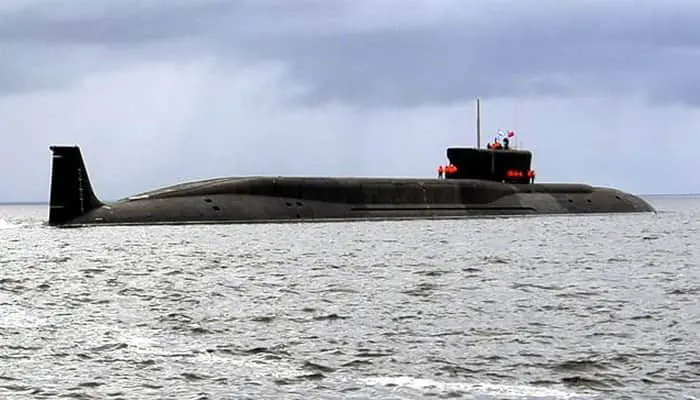

Formally known as INS Arighat (S3), the submarine was launched in November 2017 and belongs to the Arihant class of three ballistic missile submarines for the Indian Navy. The first of these, INS Arihant, was launched in 2009 and entered service in 2016, while the third, which has yet to be officially named, was launched in November 2021.
The INS Arighat was built under the Advanced Technology Vessel (ATV) project. It has a length of 111.6 meters, a beam of 11 meters, a draft of 9.5 meters, and a displacement of 6,000 tons. It can reach a maximum submerged speed of 24 knots and a surface speed of 10 knots. With a displacement of around 6,000 tons, these submarines are capable of carrying 12 K-15 ballistic missiles (SLBM) or four K-4 SLBMs, in addition to conventional torpedoes and mines. India is currently constructing two additional units.
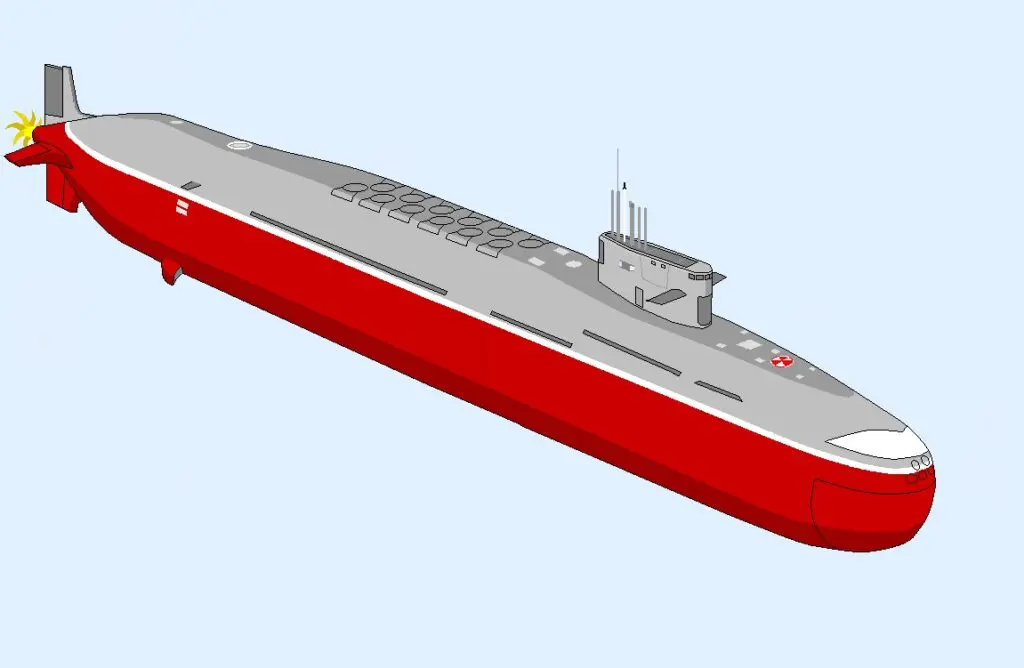
Regarding the ballistic missiles they employ, the K-15 has a range of 750 kilometers, while the K-4 can reach targets up to 3,500 kilometers away. Given their long range, the addition of the K-4 missile to the strategic nuclear arsenal would allow the Indian Navy’s ballistic missile submarines to enhance their deterrence capabilities by maintaining a presence in various locations within territorial waters or the Indo-Pacific region.
*Photographs and images used for illustration purposes.
You may also like: As part of its bid with China, the Indian Navy deploys ships in South-East Asia












