Estás usando un navegador obsoleto. No se pueden mostrar estos u otros sitios web correctamente.
Se debe actualizar o usar un navegador alternativo.
Se debe actualizar o usar un navegador alternativo.
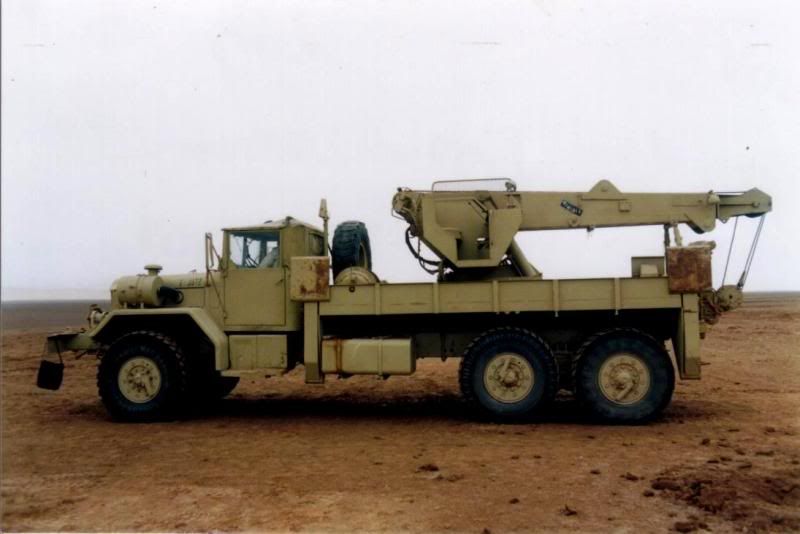
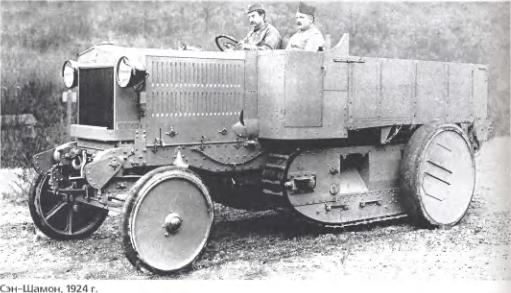
Camiones Militares
- Tema iniciado STUKA
- Fecha de inicio
Twitter
 In the 1950s the US Government had the Texan company LeTourneau design these massive wheeled land trains. If the Russians would like the railway lines they could take over and transport massive amounts of goods for long distances.
In the 1950s the US Government had the Texan company LeTourneau design these massive wheeled land trains. If the Russians would like the railway lines they could take over and transport massive amounts of goods for long distances.
The US Army had three experimental units built, the largest reaching almost 600 feet (183 m) long, which holds the record for the longest offroad vehicle. Road trains are in use in certain roles today, but the US Army examples and a few derivatives appear to be the only offroad examples built.
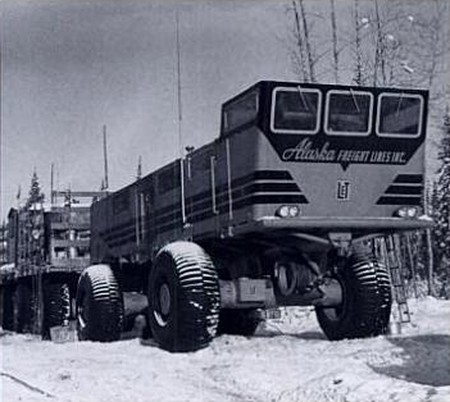
In the early 1950s, LeTourneau, a heavy-equipment maker based in Longview, Texas, developed the idea of using a diesel-electric transmission to drive multi-wheeled vehicles. Each wheel was driven by a separate electric motor, which gave the vehicles much better traction as the force of the engine was spread across a number of wheels. In general terms these vehicles were similar to the diesel-electric locomotives that were being widely introduced by the railways at the same time, but they replaced the steel wheels with rubber ones.
LeTourneau Snow Train 1
 Source
Source
LCC-1
 Source
Source
 Source
Source
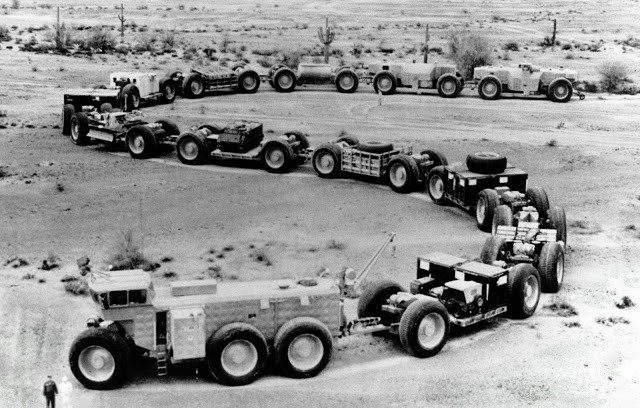
In late 1954 the Army Transportation Corps asked LeTourneau to combine the features of the Tournatrain and Sno-Buggy into a new vehicle. LeTourneau called the result the YS-1 Army Sno-Train but the Army knew it as the Logistics Cargo Carrier, or LCC-1. The LCC-1 combined the wheels of the Sno-Buggy with the power system of the Tournatrain to produce a 16×16 vehicle with one locomotive and three cars capable of handling a load of 45 tons in total.
The control cab was itself articulated into two compartments; a heated driving compartment in front for the crew of three, and a rear section containing the 600-hp diesel engine, generators and fuel tanks. The cab also sported a powered crane on the rear.
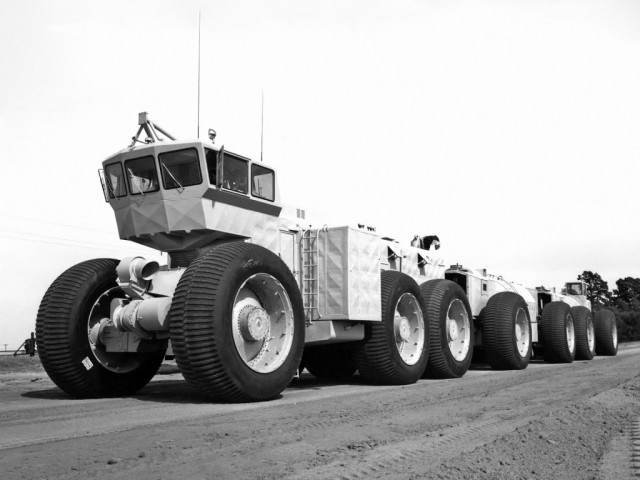
TC-497 Overland Train MkII, 1962
 Source
Source
 Source
Source
 Sou
Sou
 In the 1950s the US Government had the Texan company LeTourneau design these massive wheeled land trains. If the Russians would like the railway lines they could take over and transport massive amounts of goods for long distances.
In the 1950s the US Government had the Texan company LeTourneau design these massive wheeled land trains. If the Russians would like the railway lines they could take over and transport massive amounts of goods for long distances.The US Army had three experimental units built, the largest reaching almost 600 feet (183 m) long, which holds the record for the longest offroad vehicle. Road trains are in use in certain roles today, but the US Army examples and a few derivatives appear to be the only offroad examples built.
In the early 1950s, LeTourneau, a heavy-equipment maker based in Longview, Texas, developed the idea of using a diesel-electric transmission to drive multi-wheeled vehicles. Each wheel was driven by a separate electric motor, which gave the vehicles much better traction as the force of the engine was spread across a number of wheels. In general terms these vehicles were similar to the diesel-electric locomotives that were being widely introduced by the railways at the same time, but they replaced the steel wheels with rubber ones.
LeTourneau Snow Train 1
 Source
SourceLCC-1
 Source
Source Source
SourceIn late 1954 the Army Transportation Corps asked LeTourneau to combine the features of the Tournatrain and Sno-Buggy into a new vehicle. LeTourneau called the result the YS-1 Army Sno-Train but the Army knew it as the Logistics Cargo Carrier, or LCC-1. The LCC-1 combined the wheels of the Sno-Buggy with the power system of the Tournatrain to produce a 16×16 vehicle with one locomotive and three cars capable of handling a load of 45 tons in total.
The control cab was itself articulated into two compartments; a heated driving compartment in front for the crew of three, and a rear section containing the 600-hp diesel engine, generators and fuel tanks. The cab also sported a powered crane on the rear.
TC-497 Overland Train MkII, 1962
 Source
Source Source
Source Sou
Sou
M
Me 109
A ver quien se te hace del guapo en una esquina con un bicho de éstos-
Víctor Eduardo Barbanente
Colaborador
Cordiales Saludos
Como hacían estos Trenes offroad para que cada vagón "doblara" en el momento oportuno como para seguir una traza en "S" como la que se ve en la foto titulada "TC-497 Overland Train MkII, 1962" ????
Saludos Cordiales
Como hacían estos Trenes offroad para que cada vagón "doblara" en el momento oportuno como para seguir una traza en "S" como la que se ve en la foto titulada "TC-497 Overland Train MkII, 1962" ????
Saludos Cordiales
Que buena pregunta...!!!Cordiales Saludos
Como hacían estos Trenes offroad para que cada vagón "doblara" en el momento oportuno como para seguir una traza en "S" como la que se ve en la foto titulada "TC-497 Overland Train MkII, 1962" ????
Saludos Cordiales
Temas similares
- Respuestas
- 3
- Visitas
- 5K
- Respuestas
- 64
- Visitas
- 16K
- Respuestas
- 27
- Visitas
- 9K
- Respuestas
- 9
- Visitas
- 8K
- Respuestas
- 4
- Visitas
- 3K







.jpg)